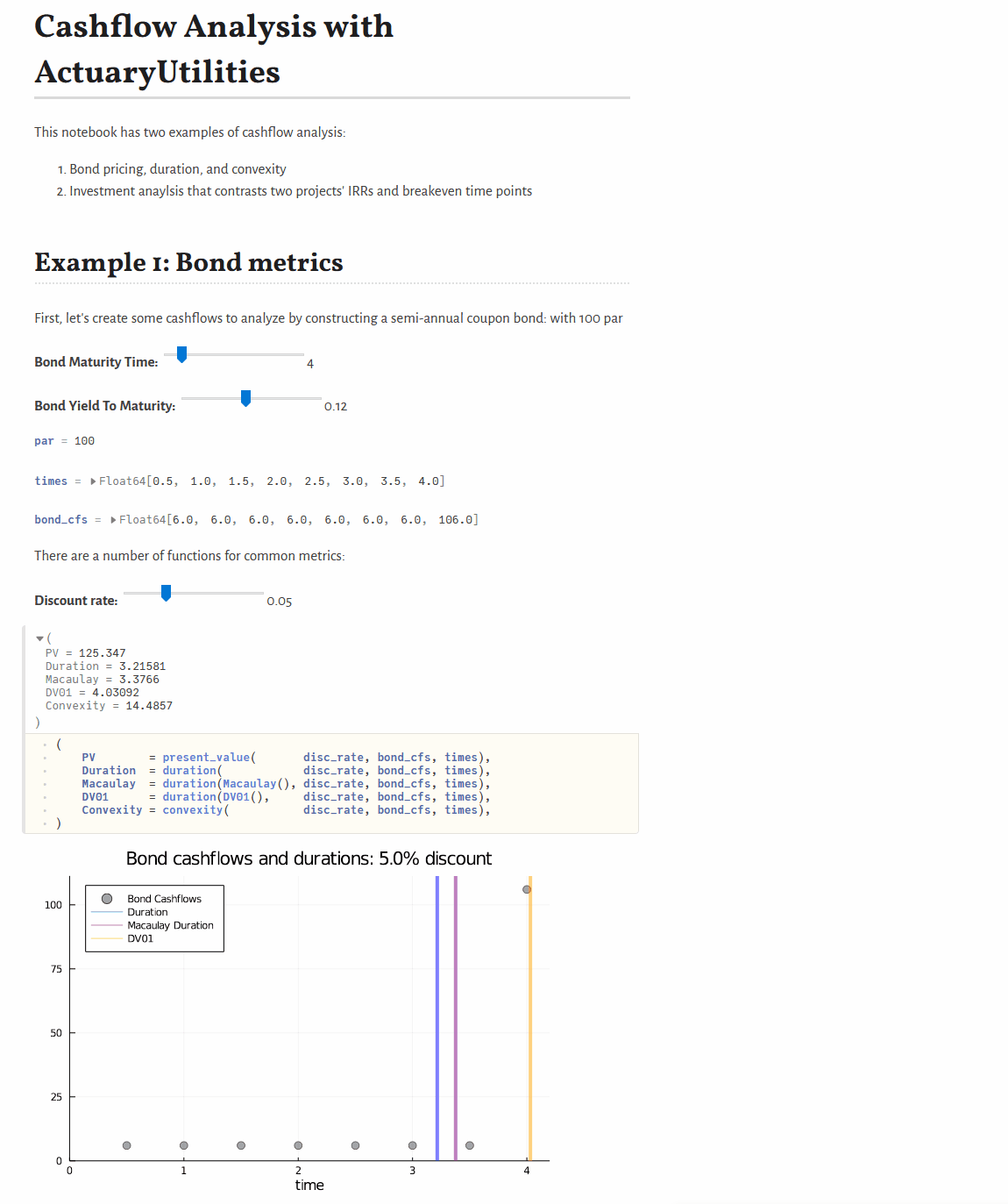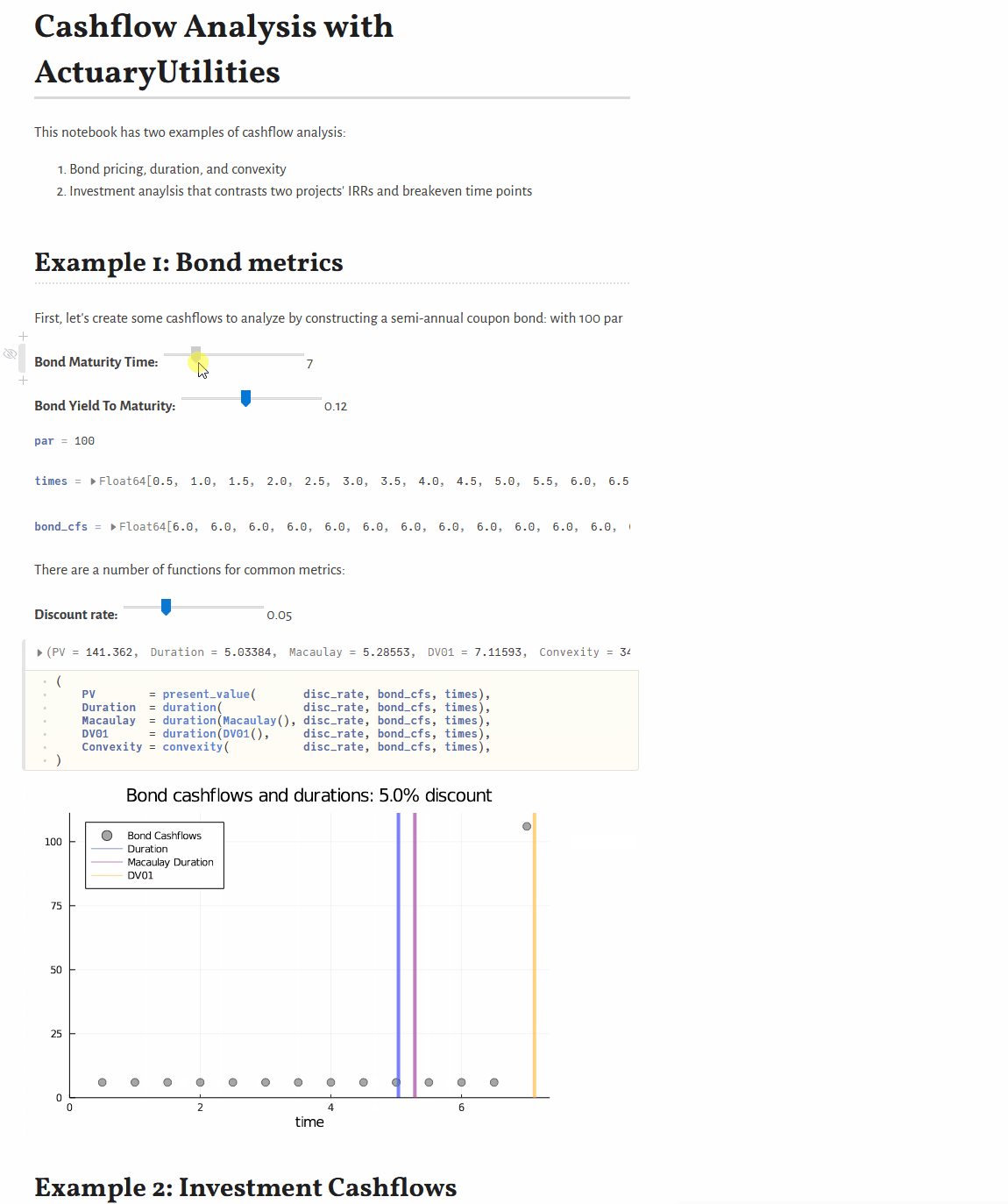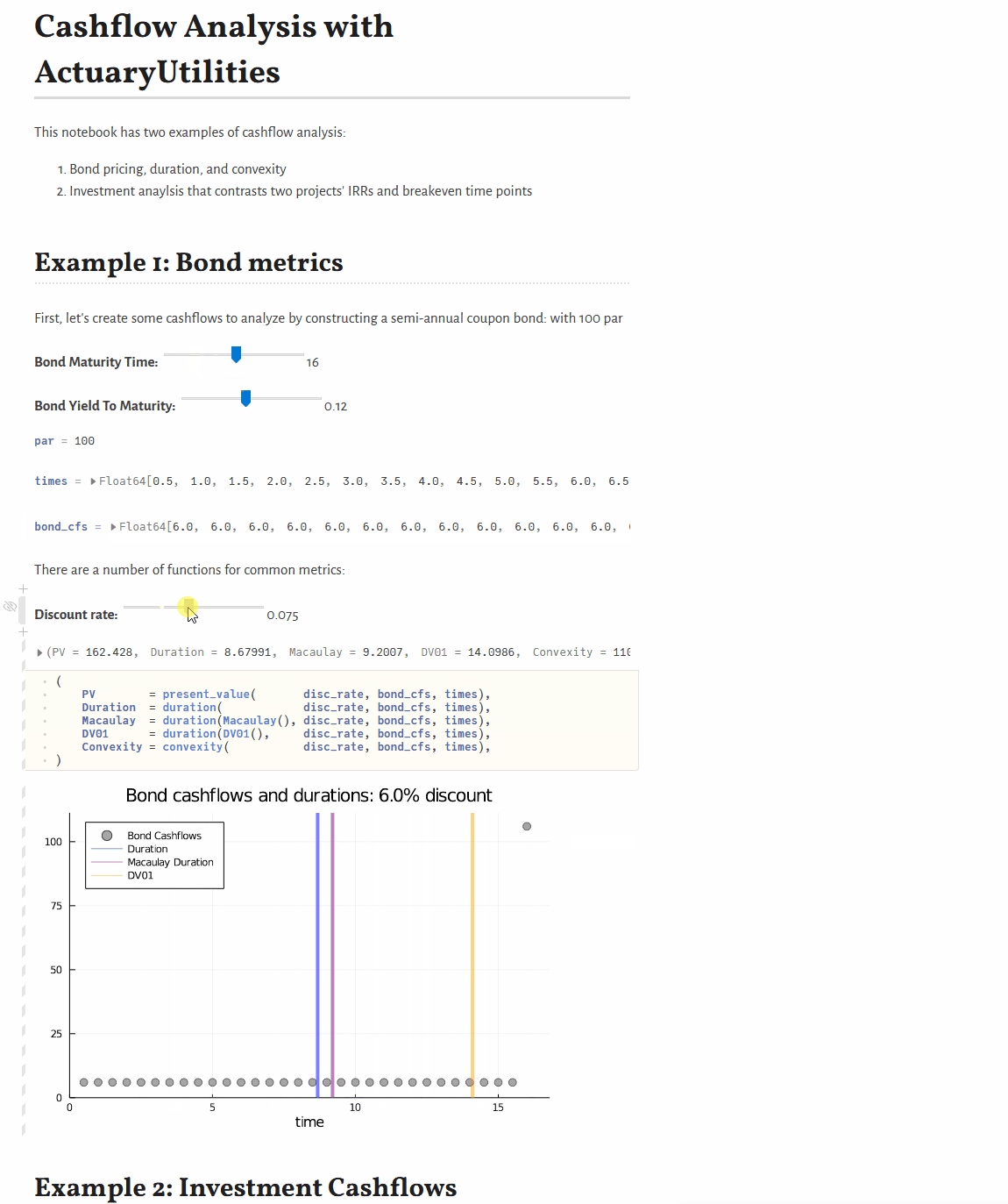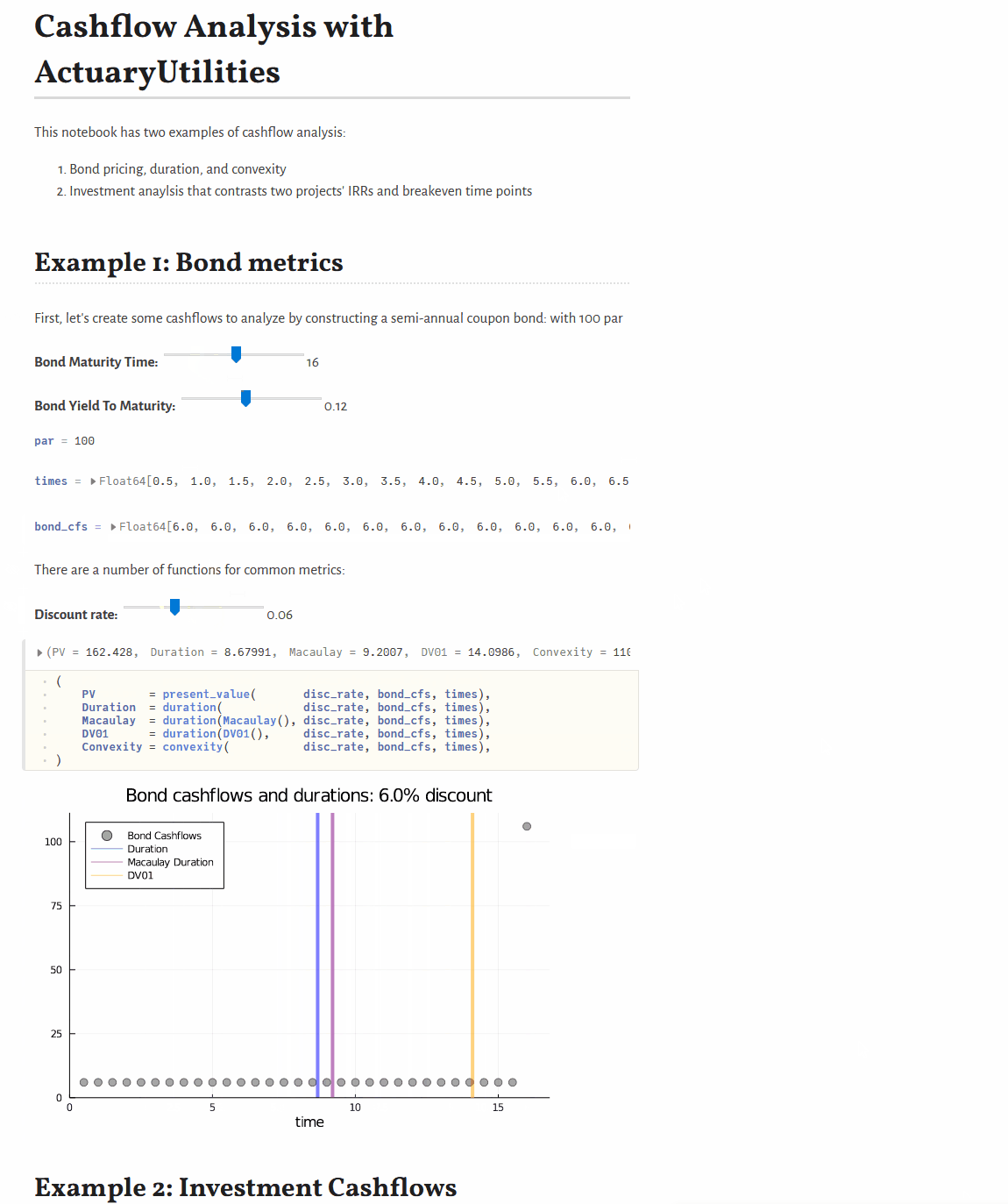
Quickstart
cfs = [5, 5, 105]
times = [1, 2, 3]
discount_rate = 0.03
present_value(discount_rate, cfs, times) # 105.65
duration(Macaulay(), discount_rate, cfs, times) # 2.86
duration(discount_rate, cfs, times) # 2.78
convexity(discount_rate, cfs, times) # 10.62Features
A collection of common functions/manipulations used in Actuarial Calculations.
Financial Maths
duration:- Calculate the
Macaulay,Modified, orDV01durations for a set of cashflows - Calculate the
KeyRate(time)(a.k.a.KeyRateZero) duration orKeyRatePar(time)duration
- Calculate the
convexityfor price sensitivity- Flexible interest rate models via the
FinanceModels.jlpackage. internal_rate_of_returnorirrto calculate the IRR given cashflows (including at timepoints like Excel'sXIRR)breakevento calculate the breakeven time for a set of cashflowsaccum_offsetto calculate accumulations like survivorship from a mortality vectorspreadwill calculate the spread needed between two yield curves to equate a set of cashflows
Key Rate Sensitivities via Automatic Differentiation
Compute exact key rate durations, DV01s, and convexities using ForwardDiff through ZeroRateCurve from FinanceModels.jl – machine-precision sensitivities in a single pass, no bump-and-reprice required.
using ActuaryUtilities, FinanceModels
rates = [0.03, 0.03, 0.03, 0.03, 0.03]
tenors = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]
zrc = ZeroRateCurve(rates, tenors)
cfs = [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 105.0]
# All key rate sensitivities in one AD pass
result = sensitivities(zrc, cfs, tenors)
result.value # present value
result.durations # key rate durations (vector)
result.convexities # cross-convexity matrixsensitivities: bundled value, key rate durations, and convexity matrix in a single AD pass- Two-curve decomposition: separate
IR01(risk-free) andCS01(credit spread) sensitivities - Do-block syntax: custom valuation functions for rate-dependent instruments (callable bonds, floaters, caps/floors)
- Hull-White stochastic model: key rate sensitivities of Monte Carlo expected values, differentiating through the full simulation pipeline
using FinanceModels: ShortRate
hw = ShortRate.HullWhite(0.1, 0.01, zrc)
hw_result = sensitivities(hw, cfs, tenors; n_scenarios=1000, rng=Xoshiro(42))
hw_result.durations # key rate durations under stochastic dynamicsSee the Key Rate Sensitivities documentation for details.
Risk Measures
- Calculate risk measures for a given vector of risks:
CTEfor the Conditional Tail ExpectationVaRfor the percentile/Value at RiskWangTransformfor the Wang TransformationProportionalHazardfor proportional hazardsDualPowerfor dual power measure
Insurance mechanics
duration:- Calculate the duration given an issue date and date (a.k.a. policy duration)
Typed Rates
- functions which return a rate/yield will return a
FinanceCore.Rateobject. E.g.irr(cashflows)will return aRate(0.05,Periodic(1))instead of just a0.05(float64) to convey the compounding frequency. This is compatible across the JuliaActuary ecosystem and can be used anywhere you would otherwise use a simple floating point rate.
A couple of other notes:
rate(...)will return the scalar rate value from aRatestruct:
julia> r = Rate(0.05,Periodic(1));
julia> rate(r)
0.05- You can still pass a simple floating point rate to various methods. E.g. these two are the same (the default compounding convention is periodic once per period):
discount(0.05,cashflows)
r = Rate(0.05,Periodic(1));
discount(r,cashflows)- convert between rates with:
r = Rate(0.05,Periodic(1));
convert(Periodic(2), r) # convert to compounded twice per timestep
convert(Continuous(2),r) # convert to compounded twice per timestepFor more on Rates, see FinanceCore.jl. FinanceModels.jl also provides a rich and flexible set of yield models to use.
Documentation
Full documentation is available here.
Examples
Interactive, basic cashflow analysis
See JuliaActuary.org for instructions on running this example.
Useful tips
Functions often use a mix of interest_rates, cashflows, and timepoints. When calling functions, the general order of the arguments is 1) interest rates, 2) cashflows, and 3) timepoints.